Sustainability
Our Sustainability Vision and Sustainability Strategy are guiding principles that inform our decisions and actions in building the future we aspire to create.
GRI 2-22 Statement on sustainable development strategy
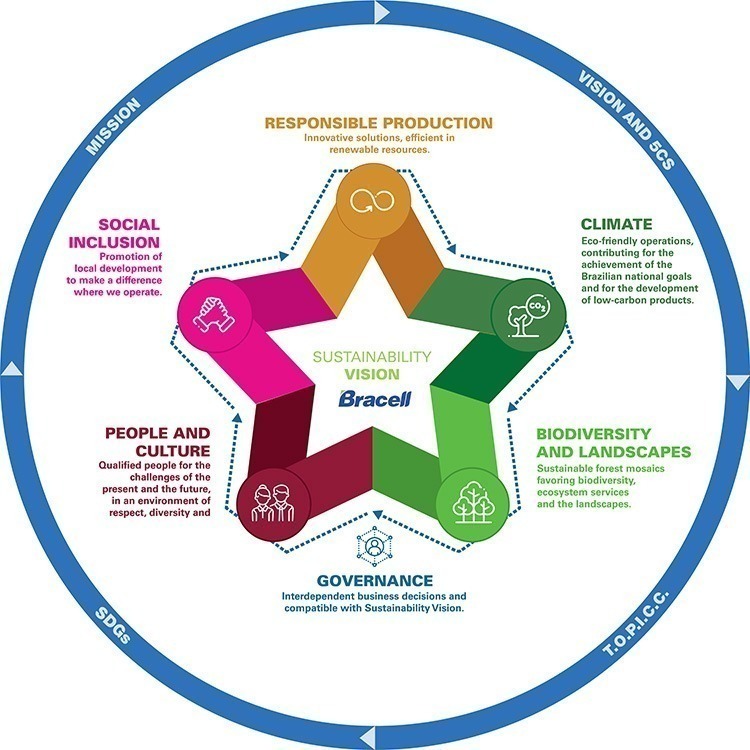
Bracell’s Sustainability Vision and Sustainability Strategy were launched in 2021 following a collaborative development effort involving our highest governance bodies and key leadership personnel. The Sustainability Strategy has been mapped to our materiality matrix, a list of material topics identified through a survey of internal and external stakeholders in 2022.
Sustainability Vision
Bracell is committed to being a sustainable business in the circular bioeconomy. We aim to revolutionize the forest-based pulp industry and remain at its forefront, while providing diversified products from responsibly managed, renewable plantations. We believe in creating shared value as well as in building impactful and long-lasting partnerships, so we may continuously do good for our communities, country, climate, customers and company.
Sustainability Strategy
Our Sustainability Strategy focuses on six pillars, covering: forestry, mill operations, people management, private social investment, decision making processes and management practices. The latter two are intersecting and are therefore integral to all other pillars in the strategy.
GRI 2-23 Policy Commitments
Bracell’s corporate governance model encourages interdependent business decisions. It is aligned with the company’s Mission and Vision, T.O.P.I.C.C. Core Values and the Code of Conduct. At the same time, it reinforces the sustainability guidelines of the company and the philosophy of creating value for the Community, Country, Climate, Customers, and Company.
Bracell’s operational management is conducted in compliance with the International Finance Corporation (IFC) standards, a global institution for the development of the private sector in developing countries; the 10 principles of the United Nations (UN) Global Compact; the UN Women’s Empowerment Principles and ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and Cerflor/PEFC certifications.
Bracell adheres to the UN Women’s Empowerment Principles (WEPs) and the Equator Principles as guidelines in managing socio-environmental risks in its projects, and follows the standards of the International Labor Organization (ILO).
Contribution to the Ten Universal Principles of the Global Compact
Human Rights
- Principle 1: Companies must support and respect the protection of internationally recognized human rights.
- Principle 2: Ensure your non-participation in violations of these rights.
Labour
- Principle 3: Companies must support freedom of association and effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining.
- Principle 4: The elimination of all forms of forced or compulsory labor.
- Principle 5: The effective abolition of child labor.
- Principle 6: Eliminate discrimination in employment.
Environment
- Principle 7: Companies must support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges.
- Principle 8: Develop initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility.
- Principle 9: Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
Anti-corruption
- Principle 10: Companies must fight corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery.
GRI 2-24 Embedding policy on commitments
Sustainability Strategy Ambassadors are part of Bracell’s sustainability governance. For each pillar of the Sustainability Strategy, there are leaders from the São Paulo and Bahia operations responsible for conducting strategy planning, connected to the programs and goals of Bracell’s Sustainability Roadmap.
In 2021, the company held a meeting with leaders to present the Sustainability Strategy, launched the same year, and to explain the alignment of the strategy key strategic socio-environmental priorities, such as climate change, biodiversity and diversity (read more in GRI disclosure 3-2).
Certifications
Bracell’s operations are certified under Cerflor/PEFC, ISO 9001:2015 (industrial production in Bahia and São Paulo) and ISO 14001:2015 (industrial production in Bahia and São Paulo, and forestry operations in Bahia). The company is also externally audited every six months against the International Finance Corporation (IFC) Performance Standards. The process is part of the due diligence involved in the financing of the two new flexible lines in Lençóis Paulista (SP) site. The external audit assesses the management of socio-environmental issues, analyzes risks and opportunities, and addresses continuous improvement action plans, when necessary.
Bracell’s operations in Bahia are also audited for Halal certifications, which guarantees the conformity of the manufacturing process to Islamic ethical and moral standards and to Islamic legislation), and Kosher standards, which ensures quality control and safety of the manufacturing process in accordance with the norms of the Orthodox Jewish diet.
Customer satisfaction, health and safety
Bracell has a procedure to monitor Customer Satisfaction, whose guidelines present criteria related to the topic and its management practices, including those relating to the health and safety of the company’s products. All manufactured products are monitored and evaluated against these requirements.
Through this procedure, the company monitors strategic indicators. These are customer-defined requirements, statutory requirements and applicable regulatory requirements (legislation and certifications). The non-conforming requirements identified, that is, those that may not be in accordance with the needs of customers and with the regulation, are addressed in a way that ensures their compliance. This process is recorded and monitored through integrated management software.
Bracell’s industrial operations are ISO 9001 certified to meet the quality requirements of the standard. This includes a focus on the customer (quality management principle, requirement 5.1.2 of ISO 9001). To this end, Bracell’s senior leadership is committed to meeting customer requirements, relevant statutory and regulatory requirements, so that they are understood and consistently met. It also ensures the management of risks and opportunities that may affect the conformity of products and services and the ability to increase customer satisfaction (ISO 9001 requirement 6.1). The requirements are controlled and monitored in the manufacturing process, the quality control processes and the sale of the product, which must be in compliance, guaranteeing customer satisfaction.
Bracell’s risk management has prevention as its first objective. The company has impact mitigation plans to reduce and neutralize risks as much as possible. Therefore, it performs an analysis of its product in relation to the potential risk to health, safety and the environment.
The pulp produced by Bracell does not present potential risks to health, safety and the environment. In compliance with legal requirements and best practices, information about all the company’s products is available to customers through Chemical Product Information Sheets with versions in Portuguese, Spanish, English, German and French. This is in accordance with the standard of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals and with the ABNT NBR 14725-4:2014 standard.
Kraft pulp, produced at the São Paulo plant, is analyzed and certified for safe applicability for the manufacture of paper and boards dedicated to food packaging and other types of paper that come into contact with food, such as support papers, filters and absorbents. At the factory in Bahia, dissolving cellulose is analyzed and certified as to its safe use in the manufacture of products that come into contact with food, such as special papers. In both cases, certification is carried out by the German laboratory ISEGA, a global reference in this area, in accordance with the relevant European and American regulations.
As in previous years, in 2021, no non-compliance related to health and safety impacts over the life cycle of the products was recorded.
GRI 2-26 Mechanisms for seeking advice and raising concerns
Bracell presents guidelines in its policies and procedures to conduct operations and activities in compliance with legislation and regulating norms. The procedures are available to all company employees and are part of the Management System.
- Among the key principles of the company’s Integrated Management Policy are the protection of and respect for the environment through the sustainable use of natural resources, the prevention, monitoring and mitigation of adverse environmental impacts arising from its activities;
- Meeting its legal requirements, norms and other commitments formally assumed by the company; and
- Ensuring an ethical relationship with all who directly or indirectly contribute to its activities, establishing active participation in the development of communities and sectors in which the company operates, maintaining open communication channels with all parties involved.
Bracell Escuta (Bracell Listens) is the channel available to all parties – internal and external – to record cases of misconduct and failure to comply with legislation. This is in line with Bracell’s Code of Conduct and the company’s internal norms. The cases are confidential, and anonymity is ensured for authors of complaints. Occurrences are evaluated by an internal audit team, which reports directly to Bracell’s board of directors and the RGE group.
Bracell Listen is available by email and phone:
bracell_escuta@bracell.com
0800 006 6012 (Bahia)
0800 033 3384 (São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul)
Bracell also makes available the Fale Conosco channel for clarifying issues, sending suggestions and compliments, in addition to registering complaints (read more in GRI disclosure 2-29). The communications are registered and addressed to the areas responsible for the subject in question, with feedback provided on the conduct of each case. The handling and solutions of the cases are also recorded (read more GRI disclosure 413-1 and 413-2). The channel is available at:
Bahia
0800 284 4747
São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul
0800 709 1490
faleconoscosp@bracell.com
Other engagement actions and forms of communication carried out by Bracell include:
- Registration of communities, with field visits to collect data;
- Impact zoning map, pinpointing Bracell’s planting areas, preservation and development areasin the territories where the company operates;
- mapping and matrix of stakeholders, people or groups directly or indirectly affected by a project and/or activity, as well as those who may have an interest in a project and/or ability to influence its outcome, positively or negatively;
- Conduction of routine meetings with communities, to promote dialogues – initial and operational – in the stages before, during and after harvest, transport and forestry operations, with the objective of keeping interested parties informed about the company’s forest management activities;
- Publication of informative materials, such as pamphlets, digital cards distributed to communities. During visits to interested parties who are impacted by forestry management, we deliver operational dialogue kits, with a bag, keychains, caps and a folder presenting the eucalyptus cycle, as well as information about Relationship with the Community and publicity of our Fale Conosco Channel.
GRI 2-28 Membership associations
As a way to integrate national and international debates and sustainability agenda, and to establish a closer relationship with stakeholders, in a spirit of collaboration and partnership, Bracell participates in a series of associations, committees, forums and unions. The main associations are listed below:
- ABAF (Bahia Association of Forestry-Based Companies)
- ABNT (Brazilian Association of Technical Standards)
- ABTCP (Brazilian Pulp and Paper Technical Association)
- ABTP (Brazilian Association of Port Terminals)
- ABTRA (Brazilian Association of Bonded Terminals and Premises)
- Alagoinhas Environmental Council
- ANEEL (National Electric Energy Agency)
- ANUT (National Association of Transport Users)
- Brazilian Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEBDS)*
- CAMCORE (Global Partners for the Future of our Forests)
- CBHRNI (Committee on the Recôncavo Norte and Inhambupe Watersheds)
- CEPRAM (State Environmental Council)
- CETESB’s Pulp and Paper Environmental Chamber
- CETREL (Liquid Effluent Treatment Center)
- CIESP Botucatu (Center of Industries of the State of São Paulo)
- COFIC (Committee for the Industrial Development of Camaçari)
- CONERH (State Water Resources Council)
- CONSEG (Community Security Council) of Esplanada-BA
- CONSENE (Northeast Public Security Council), as an invited member
- Entre Rios Environment Council
- Esplanade Environment Council
- FIEB (Federation of Industries of the State of Bahia)
- Florestar SP (São Paulo Association of Producers, Suppliers and Consumers of Planted Forests)
- Global Compact
- IBA (Brazilian Tree Industry)
- IPEF (Institute of Forestry Research and Studies)
- Lençóis River Watershed Management Committee
- Management Board of APA Joanes/Ipitanga
- Management Board of the APA of Rio Batalha
- Management Board of APA Litoral Norte
- Security Council of COFIC (Comitê de Fomento Industrial de Camaçari), as a participating member
- SIF (Society of Forestry Investigations)
- Sindpacel (Paper, Cellulose, Cardboard, Wood Pulp for Paper and Paper and Cardboard Artifacts in the State of Bahia)
- Subcommittee on the Atlantic Forest Biosphere Reserve
Since 2021, Bracell has been a member of the Brazilian Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEBDS), with participation in the Thematic Chambers for Energy and Climate Change, Biodiversity and Biotechnology, and Social Impact. CEBDS is a non-profit civil association that promotes sustainable development through engagement with governments and civil society, representing the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) network in Brazil. Bracell is also a member of the Brazilian Tree Industry (Ibá), a sectoral organization, and participates in working groups and committees.
GRI 2-29 Approach to stakeholder engagement
The relationship with stakeholders is primarily conducted by the Institutional Relations team, which works with the objective of contributing to local and regional development, through strategic partnerships with public authorities and private institutions. Bracell maintains ongoing dialogue and interactions with these parties through mapping and engagement with strategic stakeholders.
The prioritization of these audiences was based on an impact and influence analysis, which resulted in specific engagement recommendations for each of them. Employees, suppliers, communities, customers and government agencies are strategic stakeholders for Bracell.
Among the regulations of Bracell’s Integrated Management System (SIG), available to all company employees, there is a procedure for Community Relationship guidelines. Criteria and parameters are defined to establish an integrated relationship management procedure with communities neighboring Bracell’s forest and industrial management areas, in order to create a permanent relationship channel, communicate information in an up-to-date and transparent manner, identify and evaluate social aspects, define control measures and mitigation of possible negative impacts, and identify positive impacts generated by the company’s forest management operations.
The procedure identifies and presents the company’s main external stakeholders, such as customers, NGOs, communities and traditional populations and suppliers. These are stakeholders that can be positively or negatively impacted by Bracell’s activities. There are also specific relationship guidelines for communities and traditional populations, in compliance with the relevant legislation.
Among Bracell’s stakeholder mapping tools are a matrix for surveying social aspects and impacts, the socioeconomic diagnosis of communities and neighbors potentially impacted by the company’s forestry activities, an influence map with identification of geographic coordinates of communities and neighbors impacted by forestry activity, and dialogue practices with communities and neighbors directly or indirectly impacted by forest management activities (i.e.: soil preparation, planting, road operation, harvesting and transport).
The Community Relationship procedure also provides guidelines on managing demands from interested parties and other kinds of communications, such as: complaints related to the company’s operations; updates on cases that do not comply with legislation or Bracell’s Code of Ethics; operational requests such as requests from the community or neighbors to prevent possible impacts of the operation; praise; and institutional requests from government bodies, institutional meetings, associations, which must follow the management flows of Bracell’s Institutional Relations area (read more in GRI disclosure 413-1).
Bracell also has a Customer Satisfaction procedure, whose guidelines present criteria related to the topic and its management practices, including those relating to product health and safety.
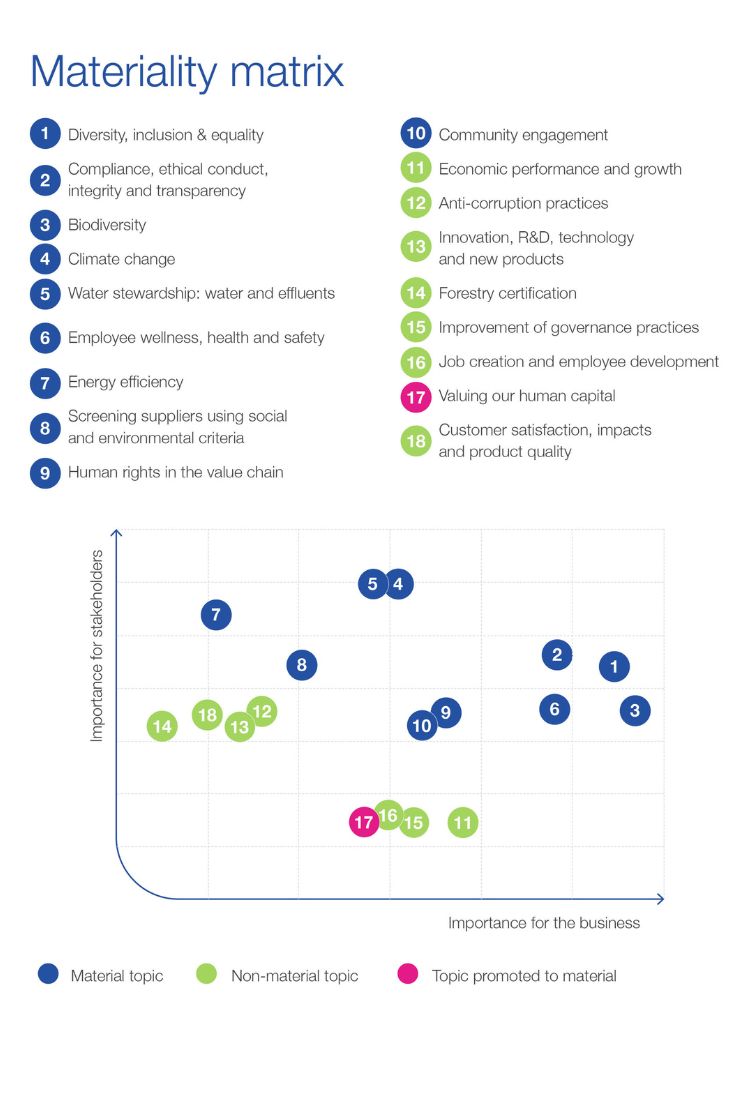
GRI 3-1 Process to determine material topics
In early 2022, Bracell conducted a process to update its materiality assessment . The study was divided into three stages:
- We reviewed industry and company documentation on sustainability and benchmarked our performance against industry peers.
- We conducted a quantitative and qualitative survey of our leadership team and key stakeholders (employees, suppliers, communities, customers and government agencies) through both interviews and survey forms.
- We selected 11 material topics that are now part of the new materiality matrix, selected by Bracell’s leadership, from a list of topics identified as the most strategic for our business.
At the end of the process, the 18 topics that scored the highest were selected based on the following references: evaluation by stakeholders via an online questionnaire; presence in the SASB sectoral materiality and in the benchmarking of the materialities of companies in the pulp and paper sector; citation by stakeholders in qualitative interviews; and the ranking of topics by customers in questionnaires addressed to the company’s commercial area.
Based on this list, a prioritization process was carried out with the participation of the leadership and ambassadors of Bracell’s Sustainability Strategy, who chose 11 material topics according to their relevance to Bracell’s stakeholders, and to the business. Among these, 10 topics received the most votes and one topic was included in the company’s materiality due to its importance to the company, namely “Valuing human capital”. The outputs of Bracell’s new materiality study were then approved by the leadership of the RGE group.
GRI 3-2 List of material topics
Materiality Matrix (Insert the materiality matrix)
Relationship between Bracell’s Sustainability Strategy, material themes updated in 2022, sustainability standards and commitments assumed by the company.
| Pillar of Bracell’s Sustainability Strategy | Material topic | GRI disclosures | SASB topics | ODS1 | Global Compact2 |
| People and Culture | Valuing human capital | 404-1, 404-2, 404-3 | 4, 5, 8, 10 | 6 | |
| Employee well-being, health and safety | 403-1, 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-5, 403-6, 403-8, 403-9, 403-10 | 3, 8, 12, 16 | |||
| Diversity, inclusion and equality | 2-7, 2-8, 405-1, 405-2, 406-1 | 3, 5, 8, 10 | 6 | ||
| Climate | Power efficiency | 302-1, 302-2, 302-3, 302-4, 302-5 | RR-PP-130a.1 | 7, 8, 12, 13 | 7, 8, 9 |
| Climate change | 201-2, 305-1, 305-2, 305-3, 305-4, 305-5 | RR-PP-110a.1; RR-PP-110a.2 | 3, 12, 13, 14, 15 | 7, 8, 9 | |
| Biodiversity and landscapes | Biodiversity | 304-1, 304-2, 304-3, 304-4 | 6, 14, 15 | 8 | |
| Responsible production3 | Evaluation of suppliers based on socio-environmental aspects | 308-1, 308-2, 414-1, 414-2; 408-1; 409-1 | RR-PP-430a.1 | 5, 8, 12, 16 | 2, 4, 5, 8 |
| Water management: water and effluents | 303-1, 303-2, 303-3, 303-4, 303-5 | RR-PP-140a.1; RR-PP-140a.2 | 6, 12 | 7, 8 | |
| Human rights in the value chain | 410-1, 412-1 | 1 | |||
| Governance | Compliance, conduct, ethics, integrity and transparency | 2-27, 205-1, 205 2, 205-3, 206-1 | 12, 16 | 8, 10 | |
| Social Inclusion | Relationship with communities | 203-1, 203-2, 411-1, 413-1, 413-2 | 1, 2 | 1 |
- SDGs to which Bracell contributes from the management of its material topics, by GRI disclosure.
- Principles of the Global Compact that Bracell complies with as a signatory based on the management of its material topics, by GRI disclosure.
- Although the topic was not identified by the stakeholders consulted as material, Bracell discloses data on its waste management due to the relevance of the topic. Therefore, this Indicator Center and Bracell’s Sustainability Report provides updates against the GRI disclosures 306-2, 306-3, 306-4, 306-5 and on the company’s respective management practices in these areas.
Comparison of the new material topics (2022) against the previous list (2016)
- Themes present in both 2016 and 2022*
- Employee health and safety
- Biodiversity
- Power efficiency
* With minor naming differences
- Themes present in 2016 and excluded in 2022
- Customer health and safety
- Reuse of materials to be discarded
- Types of materials used
- Generation of indirect economic impacts
- Good economic performance and company presence in the market
- Job generation
Themes present in 2016 and combined in a third in 2022
- Assessment of suppliers based on social impacts
- Supplier evaluation based on labor practices
- Human rights-based supplier assessments
- Ethics and compliance with (social) laws and regulations
- Compliance with laws and regulations
- Fighting corruption
- Unfair competition
- Local communities
- Non-discrimination
- Prohibition of child or slave labor
- Freedom of association
- Impacts on society
- Human rights impacts
- Water withdrawal
- Effluent and waste management
- Themes present only in 2022
- Climate change
- Respect for human rights in the value chain
- Relationship and engagement with communities
- Valuing human capital