Sustainability Strategy
In 2022, we have completed three years of operations and construction of our sustainability journey, guided by the Sustainability Policy, and by the Sustainability Vision and Strategy.
GRI 2-22 Statement on sustainable development strategy
The Bracell brand was launched in 2019, and a commitment to sustainable development lies at the heart of our business. In 2022, we celebrated three years of operations and building our sustainability journey, guided by the Bracell Sustainability Policy, Vision, and Strategy.
Check out our journey:
2003
- RGE acquires Bahia operations, in Camaçari and Alagoinhas.
2018
- RGE acquires the Lençóis Paulista operation and begins Project Star, which entails the expansion of our industrial site, through the construction of two new flexible lines, for the production of dissolving and Kraft pulp.
2019
- The Bracell brand is launched in Brazil.
- Bracell’s Sustainability Policy is updated for all Brazilian operations.
- Stakeholders are consulted and internal and external stakeholders in Bahia are engaged to identify socio-environmental risks and opportunities.
- Bracell forms Sustainability Committees.
2020
- A project is launched to develop the Bracell Sustainability Strategy and Vision, in consultation with leadership. Surveys are conducted with stakeholders, document analyses are carried out, sustainability megatrends and best practices in the sector are reviewed.
- Bracell joins the United Nation Global Compact, undertaking to annually disclose the progress made in the company`s socio-environmental management, in accordance with the 10 Universal Principles.
- Completed a multi-stakeholder social and economic assessment in 16 priority municipalities in Brazil`s southeastern state of São Paulo.
2021
- Bracell becomes a member of the Brazilian Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEBDS).
- Bracell’s Sustainability Vision and Strategy is launched, along with a short-term road map to implement key projects.
- Generation of clean electricity for the National Grid – In São Paulo we received approval for commercial energy operation, feeding between 150MW and 180MW into the National Grid, enough to meet the annual requirements of roughly three million people.
2022
- Updated a materiality assessment to identify our priority environmental, social and governance topics from the perspective of our internal and external stakeholders.
- Published Bracell’s Sustainability Report and Disclosures Hub, which complied with the 2021 GRI Standards and was independently assured1. Reported on our management approach and results across 11 material topics within our Sustainability Strategy.
- Launched the One-for-One Commitment through which we pledged to conserve one hectare of native forests for every hectare of eucalyptus plantations by 2025. These protected areas will preserve native Atlantic Forest, Cerrado and Caatinga biomes in the three states where we operate: São Paulo, Mato Grosso do Sul and Bahia.
- Bracell’s goals outlined to Brazilian Business Commitment to Biodiversity of CEBDS.
- Bracell partakes in two CEBDS initiatives in partnership with WBCSD (World Business Council for Sustainable Development): the Action for Nature Platform, and Net Zero Movement2.
- Bracell revises and prioritizes its Sustainability Strategy targets. The prioritization process embraces topics and information of material interest to ESG rating agencies, sustainability indices and our internal and external stakeholders. We also analyzed reference documents and benchmarks for the sector (national and international).
We understand that sustainability is a journey and everyday our journey progresses further. To take an important step it is necessary to lay down long-term commitments and targets, which are measurable and will be closely tracked by our senior leadership.
2023
- We have started to develop long-term socio-environmental goals. This is our commitment to the planet, to society and each and every individual, for a better and more sustainable future.
Note 1: Bracell has been publishing sustainability reports since 2010; and in accordance with GRI since 2011. From 2010 to 2017, the reports only covered the operation in Bahia. In 2018, they began covering the operations in São Paulo, and from 2021, in Mato Grosso do Sul as well. Bracell’s sustainability reports have been independently audited since 2019.
Note 2: The Action for Nature Platform is a program that strives to understand, protect and manage the dependence of participating companies and their impacts on biodiversity, by collectively implementing new frameworks, targets and international legislation. The Net Zero Movement, in turn, is a program that aims to turn corporate climate neutrality targets into reality, by practically supporting the implementation of decarbonization processes.
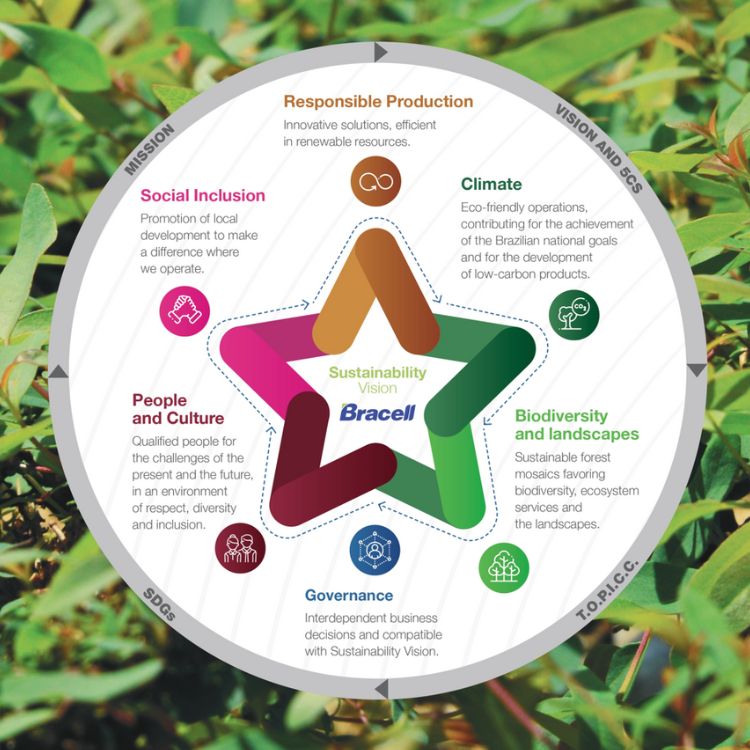
Sustainability Vision
Bracell is committed to being a sustainable business in the circular bioeconomy. We are seeking to revolutionize the forest-based pulp industry and remain at its forefront, while providing diversified products from responsibly managed, renewable plantations. We believe in creating shared value as well as building impactful and long-lasting partnerships, so we may continuously do good for Communities, the Country, the Climate, our Customers and then the Company.
Sustainability Strategy
Our Sustainability Strategy is founded upon six pillars covering environmental and social, policy and management practices: Responsible Production, Climate, Governance, Biodiversity and Thriving Landscapes, People and Culture, and Social Inclusion.
GRI 2-23 Policy commitments
Bracell’s corporate governance model encourages interdependent decision-making. The model is aligned with our Mission and Vision, our T. O. P. I. C. C. core values (Complementary Team, Ownership, People, Integrity, Customers, Continuous improvement) and our Code of Conduct. It also reinforces our Sustainability guidelines and our philosophy of creating value for Communities, the Country, the Climate, our Customers and then the Company.
Bracell’s operations are managed in line with:
- the standards set by the International Finance Corporation (IFC)—the largest global development institution focused on the private sector in developing countries;
- the Ten Principles of the United Nations (UN) Global Compact;
- the UN Women’s Empowerment Principles;
- standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and Cerflor/PEFC;
- the Equator Principles, which act as a guideline for managing social and environmental risks in our projects; and
- the standards published by the International Labor Organization (ILO).
As a signatory to Global Compact, Bracell annually discloses the progress of management and results of topics connected to the Universal Principles of the Global Compact. Click here to read the COP (Communication on Progress) of Bracell.
| Find out more about the Global Compact Universal Principles |
| Human Rights
Principle 1: Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights. Principle 2: Businesses should make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses. Employment Principle 3: Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining. Principle 4: The elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labor. Principle 5: Businesses should uphold the effective abolition of child labor. Principle 6: The elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation. Environment Principle 7: Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges. Principle 8: Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility. Principle 9: Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies. Anti-corruption Principle 10: Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery. |
How we live up to our commitments
All commitments made by Bracell are approved by senior leadership, and their guidelines are applied to operations through the Sustainability Policy, the Code of Conduct, the Code of Procurement Ethics , the Complaints Policy, and controlled internal documents such as regulations and the risk matrix and procedures, which make up the Company’s Integrated Management System (IMS) and are available to all employees.
All employees are trained and informed about Bracell’s values, commitments and policies. They also attend training on department-specific technical and operational procedures, following a role-specific training matrix also comprising Bracell’s IMS.
Bracell’s internal standards and commitments are also extended to suppliers and contractors and compliance with these standards is assessed during screening (suppliers are required to provide documentation and certificates appropriate to their scope of work), onboarding and as part of contract management.
Click here and find out more about our governance and certifications.
Risk management and due diligence
Consistent with the precautionary principle, Bracell’s risk management approach includes measures to protect the environment and prevent adverse impacts on ecosystems in its geographies. We have industry-specific indicators and programs to this end. We work to create positive environmental value in the short, medium and long term.
Our risk management processes include due diligence processes, approval of suppliers and monitoring of supplier performance and approval of third-partycompanies, presented in the Responsible Production item
GRI 2-24 Embedding policy commitments
Bracell’s Sustainability Strategy was launched along with a road map, which includes guidelines and operational objectives related to each of the Strategy’s six pillars: Responsible Production, Climate, Biodiversity and Thriving Landscapes, People and Culture, Social Inclusion and Governance.
This planning was put together and is monitored by our Sustainability Strategy ambassadors, who are leaders from the forestry, industrial, logistics (wood and pulp) operations and from the Bracell board. They also participated in the development of the Sustainability Strategy. The monitored KPIs are connected to operational and business objectives.
Certifications
Standards, certifications and pledges underpin what we do:
- Cerflor/PEFC
- ISO 9001:20151
- ISO 14001:20152
- Performance Standards of the International Finance Corporation (IFC)3
- Halal Certification4
- Kosher Certification5
Click here and see our certifications.
1In industrial production in Bahia and São Paulo.
2In industrial production in Bahia and São Paulo and our pulpwood operation in Bahia.
3Bracell is externally audited every six months against the International Finance Corporation’s Performance Standards, as part of due diligence in connection with project finance facilities for the two new flexible lines at the Lençóis Paulista (SP) site. These audits assess our management of social and environmental issues, including risks and opportunities, and inform action plans for improvement as necessary.
4 Providing assurance that our manufacturing process complies with Islamic ethics, moral, and legal standards.
5 Providing assurance that our process quality control and safety comply with Orthodox Jewish dietary laws.
Analyzing compliance in the wood chain
Bracell also undergoes client audits as part of the due diligence process for verifying controlled wood. The external auditors are supported by teams from our forestry, milling and commercial operations. The Company is evaluated on management practices and procedures in compliance with controlled wood (CW) standards.
In addition, Bracell conducts a due diligence process as part of the wood purchasing procedure, with a questionnaire applied to suppliers to ensure control of origin.The document examines documents and other evidence for compliance with local, national and international legislation.
We also monitor their practices with regard to environmental conservation and protection; endangered and protected species; land tenure and land use rights of indigenous peoples, local communities, or other affected stakeholders; health, labor and safety issues; and anti-corruption.
Customer health and safety
As in previous years, in 2022, no health and safety non-conformity impacts were recorded throughout the product life cycle.
Bracell’s risk management prioritized prevention.The Company analyses products for health, safety and environmental risks and has impact mitigation plans to neutralize and minimize their scope.
Bracell’s milling operation is carried out in compliance with standards, certifications and commitments (see the Certifications section above). It therefore meets all applicable quality requirements with a focus on the customer and manages risks and opportunities that may affect product and service conformity and the ability to increase customer satisfaction (requirements 5.1.2 and 6.1 of ISO 9001, respectively). These requirements are controlled and monitored before product sale and in the manufacturing and quality control process, ensuring customer satisfaction.
For this to be efficiently carried out, there is a commitment from senior leadership, so that all applicable requirements are understood and consistently met.
Product safety and quality analysis
- In compliance with legal requirements and best practices, information on all the company’s products is available in Chemical Product Information Sheets, with versions in Portuguese, Spanish, English, German and French. This practice complies with the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals and the standard ABNT NBR 14725-4:2014.
- Produced at the Lençóis Paulista (SP) mill, Kraft pulp is analyzed and certified for safe use in the manufacture of food packaging papers and cards and other types of materials that come into contact with food, such as base paper, filters and tissue paper. The certification is carried out by the German laboratory ISEGA, a global giant in this area, in accordance with European and US regulations.
- In the Bahia mill, the dissolving pulp is also analyzed and certified by ISEGA for safe use in the manufacture of products that come into contact with food, such as specialty papers.
- Regarding the use of chemicals, which is standard practice in the pulp and paper industry, Bracell meets all the criteria required by environmental and labor legislation, which governs the handling of these products with a focus on health and safety). With the aim of limiting the use of these inputs in the pulp manufacturing process, the new flexible lines in Lençóis Paulista (SP), inaugurated in 2021, harness new technologies that result in low chemical consumption compared to mills with older technologies. Learn about the differentials of Bracell’s new flexible lines in this infographic.
| Monitoring client satisfaction
Bracell also has a procedure to monitor customer satisfaction, with clear guidelines and criteria, including issues related to product health and safety. All manufactured products are also monitored and evaluated against these requirements. Through this procedure, the Company monitors strategic indicators, such as statutory and regulatory requirements (legislation and certifications) and others defined by the customer. Non-conforming requirements are addressed to bring them back into conformity. This process is recorded and monitored through integrated management software. |
GRI 2-26 Mechanisms for seeking advice and raising concerns
In its policies, Bracell presents guidelines and procedures for conducting its operations in compliance with legislation and regulatory standards. These regulations are available to all employees and are part of the Integrated Management System. Among the core principles of the Company’s Integrated Management Policy are:
- protecting and respecting the environment through the sustainable use of natural resources and prevention, monitoring and mitigation of adverse environmental impacts resulting from its activities;
- complying with legal requirements, standards and other commitments formally assumed by the company; and
- maintaining ethical relationships with all those who directly or indirectly collaborate with the company’s activities, actively participating in the development of the communities and sectors in which the company operates and keeping communication channels open with all involved parties.
One such channel is Bracell Escuta, a whistleblowing channel available to all stakeholders—both internal and external—for reporting misconduct and noncompliance with laws and regulations, the Bracell Code of Conduct or company standards. Cases are handled confidentially, and anonymity is guaranteed to whistleblowers. Complaints are investigated by an internal audit team, which reports directly to senior management of Bracell and RGE.
Bracell also provides a Contact Us channel to submit questions, suggestions, compliments and complaints (see more in GRI 2-29). The demands are addressed to the responsible departments by topic and the author of the report receives feedback on the handling of each case. The proceedings and solutions of the cases are recorded (read more in GRI 413-1 and 413-2).
Bracell Escuta
bracell_escuta@bracell.com
0800-006-6012 (Bahia and Sergipe)
0800-033-3384 (São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul)
Contact Us
Bahia and Sergipe
0800-284-4747
São Paulo and Mato Grosso do Sul
0800-709-1490
faleconoscosp@bracell.com
Other stakeholder engagement initiatives:
- registering communities and field visits to gather data;
- plotting an impact zoning map, with Bracell areas for planting, conservation, and development to identify impacts in these areas;
- creating and using a map and matrix of stakeholders, people or groups who are directly or indirectly impacted by a project and/or activity, and those who might have a stake in a project and/or are able to influence the outcome in a positive or negative way;
- regular meetings with communities and neighbors to foster initial and operating dialogue during and after planting, hauling and silviculture. The objective is to keep stakeholders informed about the company’s forest management activities; and
- informational materials, such as pamphlets and digital cards, are distributed to communities. During visits to stakeholders affected by forest management, an operational dialogue kit is delivered, consisting of a backpack, keychain, cap, and a brochure about the eucalyptus lifecycle. Information about Bracell’s Community Relations procedures and contact data for the “Contact Us” service are also shared.
GRI 2-28 Membership associations
In order to converge national and international sustainability debates and agendas, and to establish closer collaboration and partnership with its stakeholders, Bracell is a member of the following associations, committees, forums and unions:
- Abaf (Bahia Association of Forestry Companies)
- ABNT (Brazilian Association for Standardization)
- ABTCP (Brazilian Pulp and Paper Association)
- ABTP (Brazilian Association of Port Terminals)
- ABTRA (Brazilian Association of Customs Terminals and Warehouses)
- ANEEL (Brazilian Power Sector Regulator)
- ANUT (National Association of Freight Transportation Users)
- Cetesb Environmental Pulp and Paper Chamber
- CAMCORE (Global Partners for the Future of our Forests)
- CBHRNI (Recôncavo Norte and Inhambupe River Basin Committees)
- Cepram (State Environmental Board)
- CETREL (Wastewater Treatment Center)
- CIESP Botucatu (São Paulo State Center for Industry)
- Cofic (Camaçari Industrial Development Committee)
- Lençóis River Basin Management Committee
- CONERH (State Board for Water Resources)
- CONSEG (Public Community Security Council) of Esplanada (BA)
- Alagoinhas Environmental Board
- Entre Rios Environmental Board
- Esplanada Environmental Board
- Security Council of COFIC (Camaçari Industrial Development Committee) as a participating member
- Brazilian Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEBDS)1
- Management Board of the Joanes-Ipitanga APA
- Management Board of the Rio Batalha APA
- Management Board of the North Coast APA
- CONSENE (Public Security Council of the Northeast) as a guest member
- Fieb (Bahia State Industry Federation)
- Florestar SP (Paulista Association of Planted Forest Producers and Consumers)
- Ibá (Brazilian Forestry Association)
- Ipef (Forestry Research Institute)
- United Nations Global Compact
- Women in Forestry Network2
- SIF (Forest Investigations Society)
- Sindpacel (Union of Industries of Paper, Pulp, Cardboard, Wood Pulp for Paper and Paperboard Artifacts in the State of Bahia)
- Subcommittee of the Atlantic Forest Biosphere Reserve
1In 2021, Bracell joined the Brazilian Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEBDS), and we are currently a member of the thematic chambers on Climate & Energy, Biodiversity and Biotechnology, and Social Impact. CEBDS is a not-for-profit civil association that promotes sustainable development through advocacy in government and civil society. It represents Brazil at the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
2 In 2022 Bracell joined Rede Mulher Florestal (“Women in Forestry Network”), an independent network of female professionals and students in the forestry sector. It operates as a non-governmental, non-profit and non-partisan organization dedicated to fostering discussion around gender equity in forestry.
3 Bracell follows international guidelines that inform responsible forest management around the world and are externally audited by customers. To keep up with the agenda of best forest management practices and contribute to discussions about related strategic topics, the Company participates in national and international boards of entities linked to this topic.
GRI 2-29 Approach to stakeholder engagement
Stakeholder engagement is managed, at the highest level, by our Institutional Relations department. We help to advance development in Bracell’s geographies through strategic partnerships with governments and private organizations.
These have been prioritised through an assessment of their impact and influence, which informed stakeholder-specific engagement recommendations. Our key stakeholders include employees, suppliers, communities, customers and government agencies. Stakeholders are parties who can be positively or negatively impacted by Bracell’s operations.
| Bracell also has a procedure to monitor customer satisfaction, with clear guidelines and criteria, including issues related to product health and safety. |
Community Relations procedures
Among the regulations of Bracell’s Integrated Management System (IMS), available to all employees, are the guidelines for Community Relations. This document set outs the criteria and parameters to establish an integrated process of community relationship management for communities neighboring Bracell’s forest management and industrial areas. The regulations also present specific relationship guidelines for traditional communities and populations, complying with the relevant legislation.
The objectives are to establish a routine of ongoing dialogue, to report updated and transparent information, identify and evaluate social issues, define control and mitigation measures for possible negative impacts, and identify positive impacts.
The tools for mapping Bracell’s stakeholders include:
- a social issues and impacts assessment matrix;
- a socioeconomic diagnosis of communities and neighbors potentially impacted by the company’s forestry activities;
- an influence map plotting the geographic coordinates of communities and neighbors impacted by forestry activity; and
- dialog practices with communities and neighbors directly or indirectly impacted by forest management activities, such as land preparation, plantations, roads, harvesting and transportation).
The Community Relations procedure also presents guidelines on managing stakeholder demands such as:
- complaints related to the company’s operations
- reports of breaches of the legislation or the Bracell Code of Conduct
- operational requests such as community or neighbor requests to forestall potential operational impacts
- compliments
- institutional requests from government agencies and meetings of institutions or associations. Such demands must follow the management flows of Bracell’s Institutional Relations function (read more in GRI 413-1).
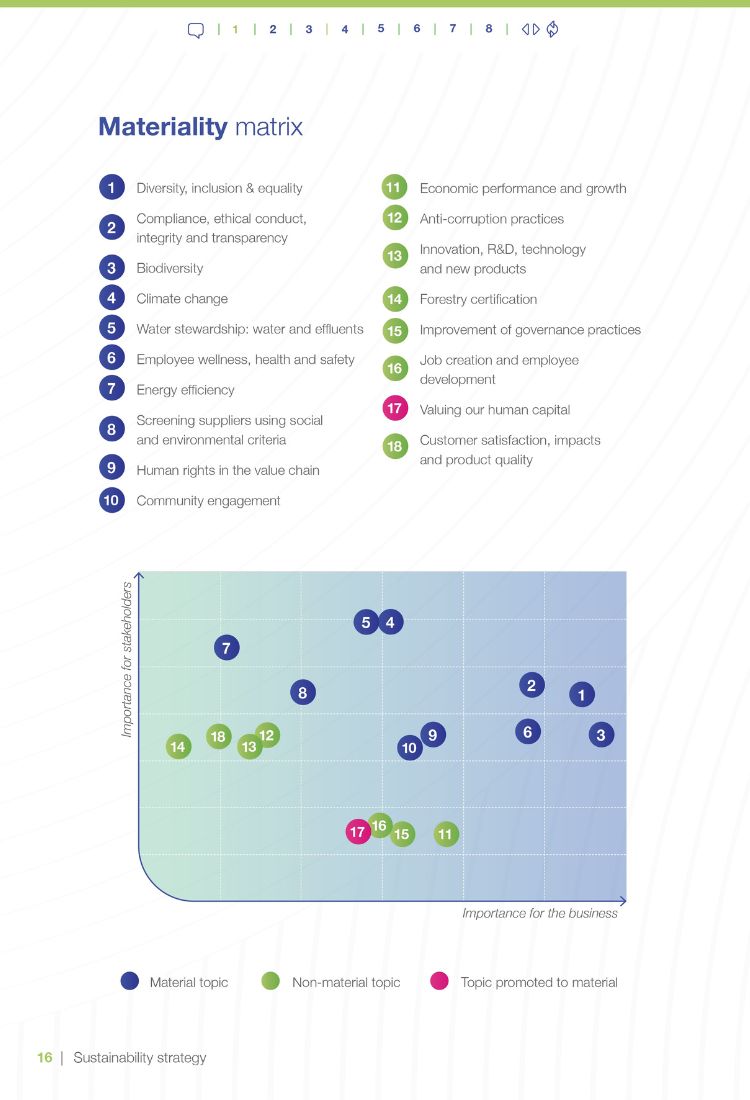
GRI 3-1 Process to determine material topics
In early 2022, Bracell carried out an exercise to update its materiality matrix. The assessment was structured into three steps:
- We reviewed industry and company documentation on sustainability, and benchmarked our performance against industry peers;
- We conducted a quantitative and qualitative survey among our leadership team and key stakeholders (employees, suppliers, communities, customers and government agencies) through both interviews and survey forms; and
- Bracell leadership selected 11 material topics to compile its materiality matrix, based on a list of 18 topics identified as the most strategic.
The materiality study involved consultation with a range of Bracell stakeholders – company leaders, suppliers, pulpwood producers, customers, local communities, government representatives and sectoral organization representatives.
The final list of topics (18) was created by selecting those that scored the highest based on the following benchmarks: a stakeholder evaluation via online questionnaire; presence in the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) sectoral materiality and materiality benchmarking of pulp and paper industry companies; stakeholder mentions in qualitative interviews; and ranking of topics demanded by customers in questionnaires addressed to the company’s sales department.
A prioritization process was implemented based on this list, with the participation of the Bracell Sustainability Strategy ambassadors and leadership, who chose 10 material topics according to their importance to stakeholders and the business. One topic was added for its importance to the company (Employee recognition). The new Bracell materiality matrix was also approved by RGE Group leadership.
GRI 3-2 List of material topics
Relationship between Bracell’s Sustainability Strategy, the material topics updated in 2022, sustainability standards, and commitments made by the Company
| Sustainability Strategy Pillar | Material topic | GRI Disclosures | SASB Disclosures | SDG1 | Global Compact2 |
| People & Culture | Valuing our human capital | 404-1, 404-2, 404-3 | 4, 5, 8, 10 | 6 | |
| Employee health, safety and well-being | 403-1, 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-5, 403-6, 403-8, 403-9, 403-10 | 3, 8, 12, 16 | |||
| Diversity, Inclusion & Equality | 2-7, 2-8, 405-1, 405-2, 406-1, | 3, 5, 8, 10 | 6 | ||
| Climate | Energy efficiency | 302-1, 302-2, 302-3, 302-4, 302-5 | RR-PP-130a.1 | 7, 8, 12, 13 | 7, 8, 9 |
| Climate change | 201-2, 305-1, 305-2, 305-3, 305-4, 305-5 | RR-PP-110a.1, RR-PP-110a.2 | 3, 12, 13, 14, 15 | 7, 8, 9 | |
| Biodiversity and landscapes | Biodiversity | 304-1, 304-2, 304-3, 304-4 | 6, 14, 15 | 8 | |
| Responsible production3 | Screening suppliers using social and environmental criteria | 308-1, 308-2, 408-1, 409-1, 414-1, 414-2 | RR-PP-430a.1 | 5, 8, 12, 16 | 2, 4, 5, 8 |
| Water stewardship: water and effluents | 303-1, 303-2, 303-3, 303-4, 303-5 | RR-PP-140a.1, RR-PP-140a.2 | 6, 12 | 7, 8 | |
| Human rights in the value chain | 410-1 | 1 | |||
| Governance | Compliance, ethical conduct, integrity and transparency | 2-27, 205-1, 205-2, 205-3, 206-1 | 12 ,16 | 8, 10 | |
| Social Inclusion | Relations with communities | 203-1, 203-2, 411-1, 413-1, 413-2 | 1, 2 | 1 |
- SDGs we support through our material topics, by GRI disclosure.
- Global Compact Principles we uphold as a signatory by addressing our material topics, by GRI disclosure.
- Although stakeholders have not identified this topic as being material, we continue to report on waste management given the relevance of this topic. Bracell’s Disclosures Hub and Sustainability Report therefore include GRI disclosures 306-2, 306-3, 306-4, 306-5 and a corresponding description of our management approach.
- Although not directly linked to Bracell’s material topics, disclosures 201-2 (Financial implications and other risks and opportunities due to climate change), 203-1 (Infrastructure investments and services supported and 203-2 (Significant indirect economic impacts) are related to topics that are strategic for Bracell’s value chain. For this reason our management approach and performance for these disclosures have been reported in our 2022 Sustainability Report.
Comparison between the new materiality matrix (2022) and the previous version (2016)
1. Topics present in both 2016 and 2022*
- Employee health and safety
- Biodiversity
- Energy efficiency
* With slight differences in nomenclature
2. Topics present in 2016 but not in 2022
- Customer health and safety
- Recycling of disposable materials
- Type of materials used
- Indirect economic impacts generated
- Sound economic performance and market footprint
- Job creation
3. Topics present in 2016 and 2022
- Assessment of suppliers’ social impacts
- Assessment of suppliers’ labor practices
- Assessment of suppliers’ human rights performance
- Ethics and compliance with legislation and regulations (social)
- Compliance with laws and regulations
- Fighting corruption
- Unfair competition
- Local communities
- Non-discrimination
- Prohibition on child or slave labor
- Freedom of association
- Complaints about impacts on society
- Complaints about impacts on human rights
- Water withdrawal
- Waste and wastewater management
4. Topics present in 2022 only
- Climate change
- Human rights in the value chain
- Community relations and engagement
- Employee recognition